The large-scale Shagehuang photovoltaic base project generally utilizes 35kV cables to gather the power output from the local step-up transformers of each power block to the substation.
As the cost of a 35kV cable per meter is several hundred currency, and the usage amount is approximately 200km/GW, the total cost reaches around 50 million currency per GW (with significant regional variations), making it one of the key points for cost control.
The optimization of a 35kV cable route involves at least two aspects:
- l Group transformers to a predetermined quantity of circuits
- l How are these transformers connected to each other
To this end, based on the Depth-First Search (DFS) algorithm, this paper proposes a systematic solution centered around the allowable cable length between transformers, with the goal of minimizing total cost or shortening the total path. This solution has been implemented in Candela3D software.
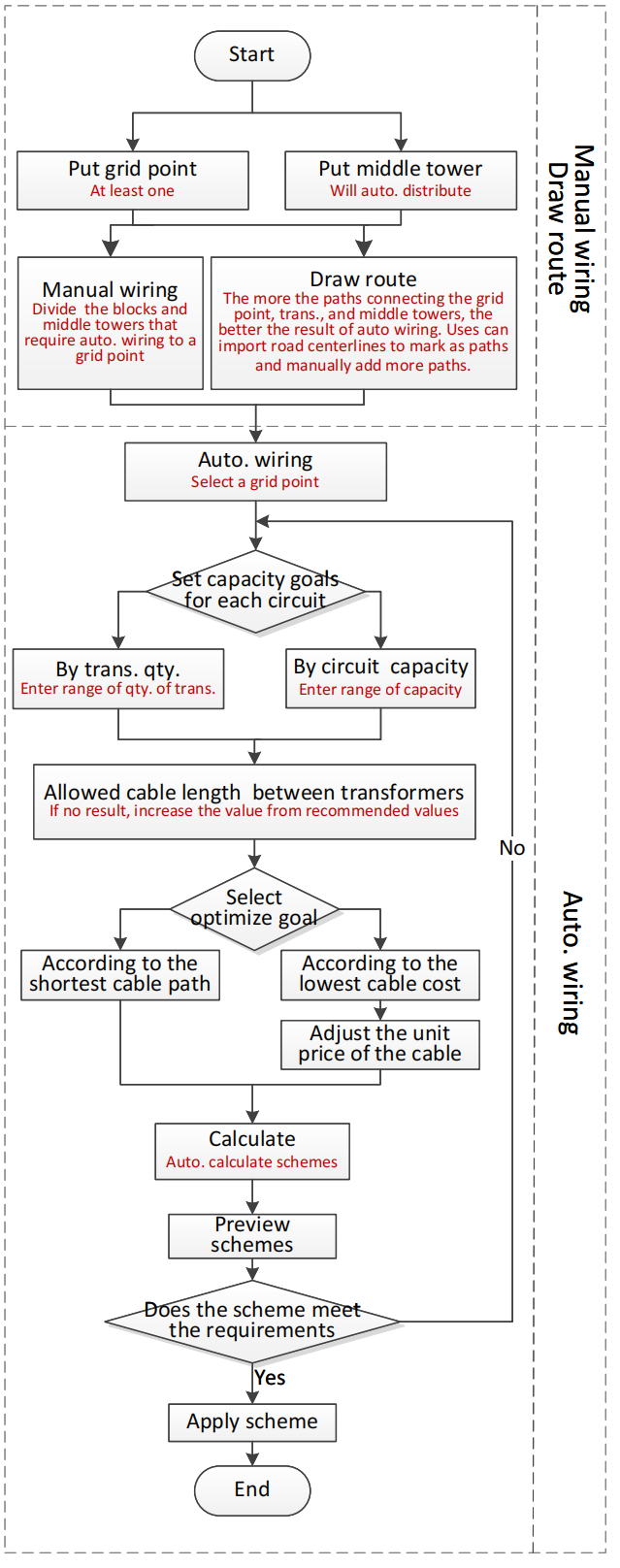
Workflow
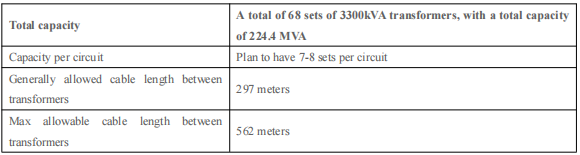
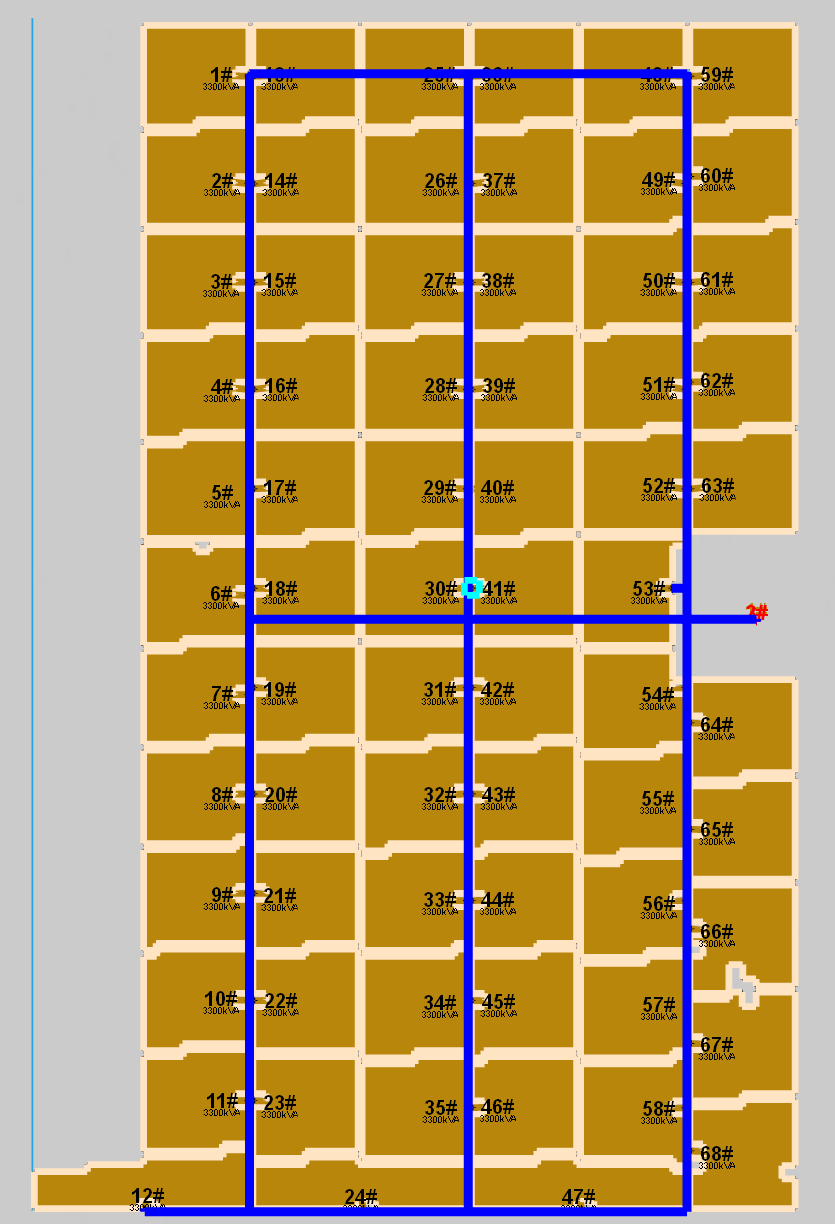
Practical case
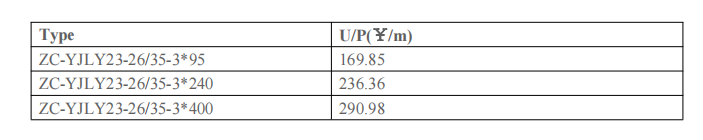
The following three types of Aluminum alloy cables are used in the setting. The cable section is automatically selected by the software based on the combination of plans, connection relationships, cable ampacity, and laying factors.
Optimization results
After the software has Calculate for 5 Minutes and traversed tens of millions of possible combination plans, the top 10 plans sorted by CPEX from low to high are as follows:
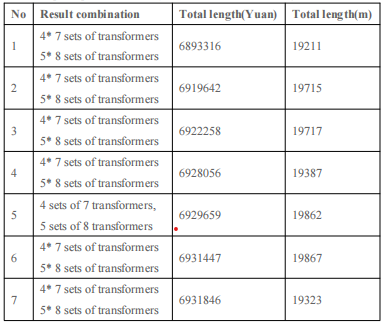
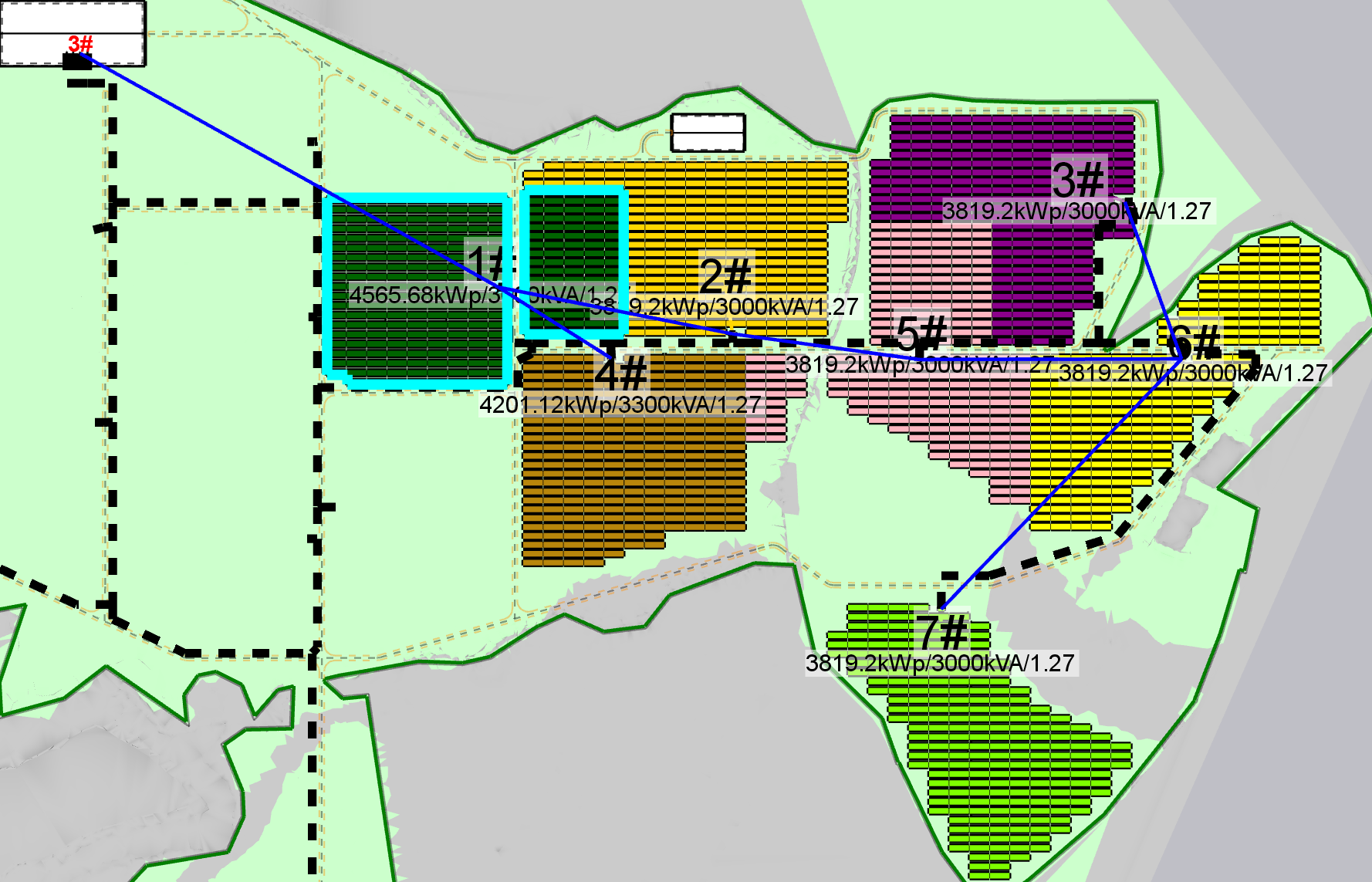
The plan with the lowest CPEX is as follows:
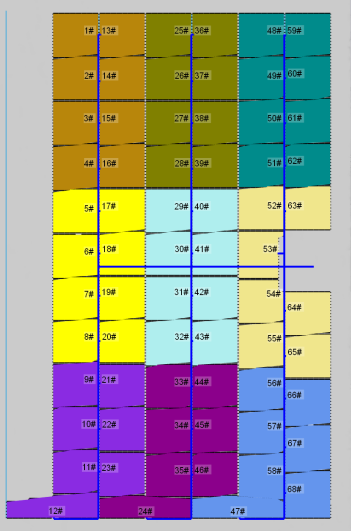
Result verification
The user manually adjusted the Combine plan as follows:
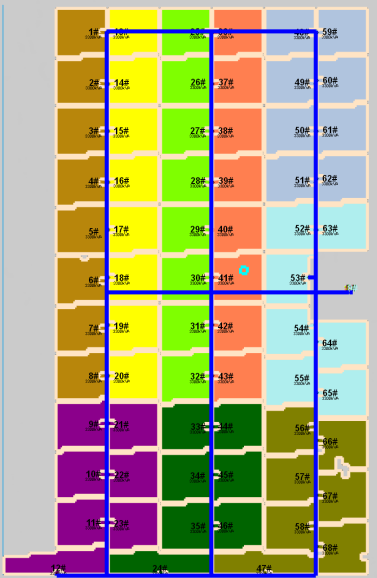
After Calculate, the total CPEX of this plan is 7,226,381 currency, which is 333,065 currency higher than the optimal plan.
Auto-select the optimal connection relationship
After determining which transformers are connected to a certain circuit, it is also necessary to decide how the transformers should be connected to each other.
The following diagram illustrates the approach of starting from the transformer closest to the grid point and connecting subsequent transformers in a proximity-based manner:
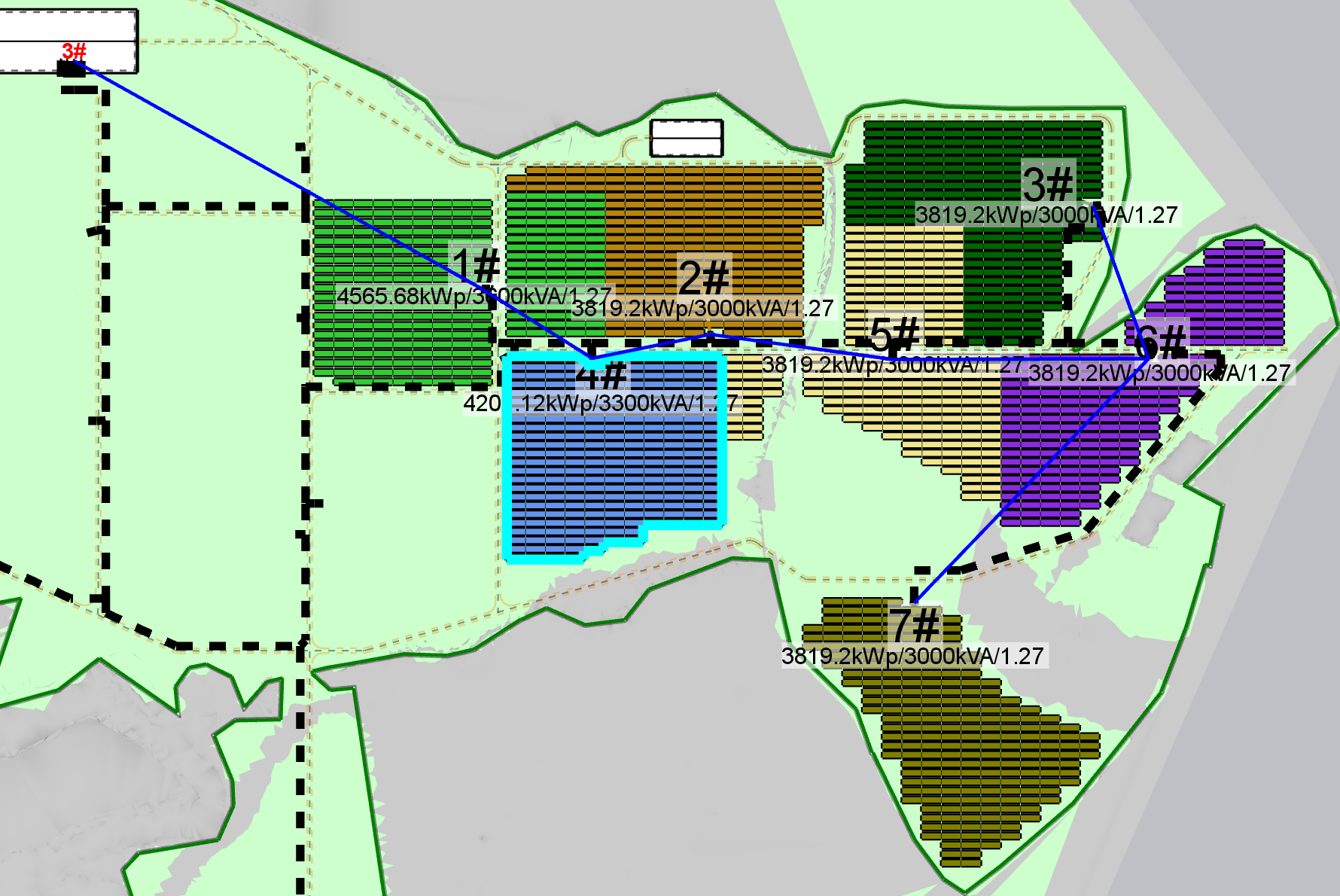
Through AUTO wiring, select the same circuit, the software will select the optimal connection based on cable section, Length, and CPEX. The results are as follows:

Summary
This article proposes an optimization solution for medium voltage cable convergence based on the Depth-First Search (DFS) algorithm. The core control variable is the allowable cable length between transformers, with the goal of minimizing total CPEX or shortening the total path. This solution can significantly reduce project CPEX and enhance design efficiency through optimizing convergence and connectivity.
Article Comments(0)